Forex Trading 101: How the World’s Largest Market Works for Indian Investors in 2025
Picture exchanging ₹1,000 for US dollars at a local shop, betting the rupee will strengthen to make a profit that’s the heart of forex trading. With a $7.5 trillion daily turnover globally (BIS, 2024) and India’s GDP growing at 6.2% in 2025 (RBI estimate), the foreign exchange (forex) market is a dynamic arena for investing in India. Overseen by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), forex trading offers opportunities but is risky SEBI’s 2024 study shows 85% of retail traders lose money. This beginner’s guide simplifies forex trading in India, using real-world examples and practical tips to help you navigate the world’s largest market. Whether you’re funding health insurance or diversifying your personal finance, let’s explore forex in 2025!
1. What Is Forex Trading?
Forex trading involves buying one currency and selling another to profit from exchange rate changes. In India, it’s tightly regulated by RBI and SEBI to ensure transparency and investor protection.
- Key Features:
- World’s Largest Market: $7.5 trillion daily turnover (BIS, 2024).
- Currency Pairs: Traded in pairs (e.g., USD/INR, EUR/USD).
- Decentralized: Trades via brokers, not a central exchange.
- 24/5 Trading: Open Monday 5 p.m. IST to Saturday 4 p.m. IST.
- India Context:
- Regulated by RBI (manages $676B forex reserves) and SEBI (oversees 20 crore demat accounts, 2025 estimate).
- Only INR-based pairs (e.g., USD/INR) allowed for retail traders.
- Analogy: Like swapping ₹1,000 for USD, hoping INR strengthens to gain ₹100.
- Risk Alert: SEBI’s 2024 Retail Trading Analysis reports 85% of forex traders lose money due to leverage.
Why It Matters: Forex diversifies beyond stocks or bonds, but it’s riskier than money market investments .
2. How Does Forex Trading Work?
Forex trading means speculating on currency price movements. You buy a pair if the base currency (first) will strengthen against the quote currency (second).
- Key Concepts:
- Currency Pairs:
- Base: First currency (e.g., USD in USD/INR).
- Quote: Second (e.g., INR in USD/INR).
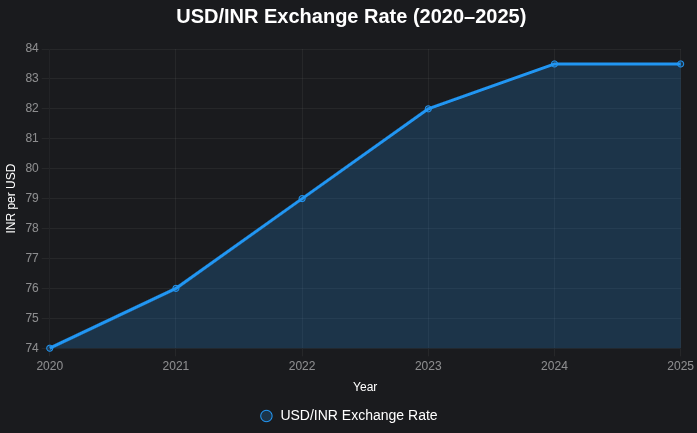
- Example: USD/INR = 83.50 means ₹83.50 buys 1 USD.
- Leverage: Trade large positions with small capital (e.g., 10:1).
- Pips: Smallest price move (e.g., 83.50 to 83.51 = 1 pip).
- Spread: Broker’s fee (e.g., 2–3 pips for USD/INR).
- Currency Pairs:
- Example (Illustrative):
- You expect USD/INR to rise from 83.50 to 84.00 (RBI data, 2024 trend).
- Buy 1 lot (1,000 units) of USD/INR with 10:1 leverage (₹8,350 margin).
- If USD/INR hits 84.00, profit = ₹500 (50 pips × ₹10/pip, minus fees).
- If it falls to 83.00, loss = ₹500.
- India Fact: USD/INR dominates; ₹5,000 crore daily turnover on NSE (2024, SEBI estimate).
3. Types of Currency Pairs
Forex pairs vary by liquidity and volume:
- Major Pairs:
- Involve USD (e.g., USD/INR, EUR/USD).
- Low spreads (2–3 pips), high liquidity.
- Example: USD/INR is India’s most traded pair.
- Minor Pairs:
- No USD (e.g., EUR/GBP).
- Higher spreads (5–10 pips).
- Exotic Pairs:
- Major + emerging currency (e.g., USD/THB).
- High spreads (10–20 pips).
- Example: INR/ZAR (South African rand).
Insight: Beginners should trade USD/INR, regulated by RBI for stability.
4. Why Is Forex Trading Popular in India?
With India’s 6.2% GDP growth and 20 crore demat accounts (SEBI, 2025), forex trading is booming due to:
- High Returns Potential:
- Leverage (10:1 to 50:1) amplifies profits (e.g., ₹500 on ₹8,350 margin).
- Example: Priya earns ₹1,000 on USD/INR with ₹5,000.
- Hedging Opportunities:
- Protect against INR depreciation (e.g., importers buy USD/INR futures).
- Links to futures and options.
- Accessibility:
- Start with ₹5,000 via SEBI-registered brokers like Zerodha.
- RBI oversees $676B forex reserves, ensuring stability.
- Global Exposure:
- Trade USD, EUR, not just INR, unlike mutual funds.
Caution: SEBI’s 2024 study reports ₹10,000 crore in retail forex losses annually.
5. Risks of Forex Trading
Forex is high-risk know these:
- Leverage Losses:
- 10:1 leverage means a 10% drop wipes out your margin.
- SEBI: 85% of traders lose money (2024).
- Volatility:
- USD/INR swung 3% in Q2 2024 (RBI).
- Fix: Use stop-loss orders.
- Broker Fees:
- Spreads (2–10 pips) and ₹20–40/trade (Zerodha, 2024; check 2025 rates).
- Fix: Choose low-spread brokers.
- Complexity:
- Requires understanding pips and RBI policies (e.g., 5.5% repo rate).
- Fix: Practice with Zerodha’s demo account.
- Scams:
- Unregulated brokers promise “guaranteed returns.”
- Fix: Use SEBI-registered brokers (see upcoming “Avoiding Scams” post).
Example: Anil loses ₹10,000 on USD/INR after an RBI rate cut; a stop-loss could’ve saved ₹8,000.
6. Who Should Trade Forex?
Forex suits:
- Experienced Investors: Know markets, risks .
- Hedgers: Importers/exporters managing INR volatility.
- Risk-Takers: Willing to lose ₹5,000–50,000.
- Not for Beginners: Start with bonds or money market .
Example: Priya, a 30-year-old from Delhi, uses forex to hedge her US study abroad loan, saving ₹20,000 during INR depreciation.
7. How to Start Forex Trading in India 2025
Ready? Follow these steps:
- Learn the Basics
- Understand pairs (USD/INR), pips, leverage.
- Read RBI’s forex guide .
- Try Zerodha’s demo trading.
- Assess Risk Tolerance
- Can you lose ₹5,000–25,000? If not, try mutual funds.
- Use NSE’s risk calculator.
- Open a Trading Account
- Platforms: Zerodha, Upstox, Angel One (SEBI-registered).
- Process: KYC with PAN, Aadhaar (10 mins).
- Cost: ₹200–500 opening; ₹5,000 margin.
- Choose a Currency Pair
- Beginners: USD/INR (2–3 pip spreads).
- Check: Lot size (1,000 units), margin (10–20%).
- Tools: Moneycontrol, RBI website.
- Start Trading
- Start small: ₹5,000 for 1 lot USD/INR.
- Example: Buy USD/INR at 83.50; sell at 84.00 for ₹500 profit.
- Use stop-loss to cap losses.
- Monitor and Learn
- Track via Zerodha Kite app.
- Follow RBI’s 5.5% repo rate, US Fed policies.
- Review monthly: Avoid over-trading (SEBI: 85% lose).
8. Forex Trading in India 2025: Trends and Opportunities
- Growing Volume: ₹5,000 crore daily forex turnover on NSE (2024, SEBI estimate).
- Regulatory Strength: RBI manages $676B forex reserves; SEBI enforces transparency.
- Digital Platforms: Zerodha, Upstox simplify trading.
- USD/INR Dominance: 70% of India’s forex volume (NSE, 2024).
- RBI Policies: 2024 FPI-to-FDI reclassification and ₹1.5 lakh crore liquidity surplus boost trading (RBI, 2024).
9. Forex vs. Other Markets
| Market | Risk Level | Returns Potential | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forex | High | High (leverage) | Hedging, speculation |
| Stocks | Medium | Moderate (10–15%) | Long-term growth |
| Bonds | Low | Low (5–7%) | Safety |
| Mutual Funds | Medium | Moderate (8–12%) | Diversification |
Insight: Harvard studies (2023) show forex leverage increases loss risk by 4x vs. stocks .
10. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- What is forex trading?
Buying/selling currencies to profit from exchange rate changes. - Is forex trading legal in India?
Yes, via SEBI-registered brokers like Zerodha; only INR pairs allowed (RBI). - How much capital for forex trading?
₹5,000–25,000 for beginners (Zerodha, 2024). - Is forex safe for beginners?
No, 85% lose money (SEBI, 2024). Try mutual funds . - How does forex fit into personal finance?
Hedge currency risks; not for goals like health insurance.
11. Conclusion
Forex trading is like a T20 cricket match fast, exciting, but risky. With India’s 6.2% GDP growth, $676B forex reserves (RBI), and 20 crore demat accounts (SEBI, 2025), the forex market offers high rewards but 85% of traders lose money (SEBI, 2024). Beginners should master stocks, bonds, or mutual funds first. If ready, start with ₹5,000 on Zerodha, use stop-losses, and pair forex with money market funds to fund health insurance . Trade smart in 2025!